Precipitation is the liquid or solid state of water particles that fall into the atmosphere. Rain, hail and snow are various forms of precipitation. Weather radars can locate precipitation (rain, snow, hail) and measure its intensity in real time.
AERIS has access to data from Météo-France weather radars, as well as from other projects studying precipitation:
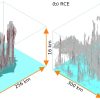
Scientific context C²OMODO (Convective Core Observations through MicrOwave Derivatives in the trOpics) is a CNES space project, a tandem of radiometers that will be launched in March 2030, as part […]

AERIS provides access to radar data from the Météo-France French operational network in mainland France and overseas. The radar data is made up of four products: AERIS manages the conversion […]
The CORSiCA Platform for Atmospheric Observations (PCOA) of the Aerology Laboratory is located in Corsica on about fifteen sites to respond to the different themes studied by participants from several […]

The Mediterranean region is currently identified as one of the future “hot spots” by climate modelling, indicating a strong decrease in precipitation during the summer period. However, these results are […]

HyMeX aims at a better understanding, quantification and modelling of the hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean, with emphasis on the predictability and evolution of extreme weather events, inter-annual to decadal […]
The first AMMA observation campaign was successfully carried out from mid-January to mid-February. It enabled the characterisation of the microphysical and radiative properties of aerosols and their dynamics during the […]

Megha-Tropiques is a space mission jointly managed by the space agencies CNES and ISRO. This mission is designed to study the convective systems of the atmosphere and more particularly the analysis of the water cycle through the transport and distribution of water vapor, the life cycle of convective systems and energy exchanges in the equatorial belt. The tropical zones are those where the most important energy exchanges occur: radiative exchanges, latent heat exchanges, transport of constituents and energy through dynamic processes. The challenge is therefore to increase knowledge of hydrological and energy processes in the tropics and their influence on the global circulation of the atmosphere, that the oceans, and climatic variations.

CloudSat is a NASA satellite. It is studying clouds in detail to better characterize the role they play in regulating Earth’s climate. It is providing a global survey of the vertical structure and overlap of cloud systems and their liquid and ice-water contents.

The FROGS (Frequent Rain Observations on GridS) database consists of a collection of precipitation products from various origins (in-situ, reanalysis and satellite) with a homogeneous format, all set to the […]

