A cloud is a hydrometeor consisting of a suspension in the atmosphere of tiny particles of liquid water or ice, or both, and generally not touching the ground. It can also include larger particles of liquid water or ice, as well as non-aqueous liquid particles or solid particles from, for example, industrial fumes, smoke or dust.
The AERIS cluster has numerous research projects studying clouds, which you can find here :
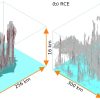
Scientific context C²OMODO (Convective Core Observations through MicrOwave Derivatives in the trOpics) is a CNES space project, a tandem of radiometers that will be launched in March 2030, as part […]

The ANR ICCARE project (Ice Crystals in deep convective Clouds: interaction with Aerosols, Radiation and Electricity; https://anr.fr/Project-ANR-21-CE01-0006, 2022-2026) aims to better understand how ice crystals interact with aerosols, cloud microphysics, […]

The ERC1 funded MAESTRO project aims to answer this question by addressing the following goals: As part of this project, an airborne field campaign will be organized to collect the observations needed to […]

ACTRIS-FR is the French component of ACTRIS-EU for the observation and exploration of aerosols, clouds and reactive gases and their interactions. ACTRIS is a distributed European research infrastructure supporting research […]
SAETTA (Suivi de l’Activité Electrique Tridimensionnelle Totale de l’Atmosphère) detects and localizes in three dimensions the electromagnetic radiation emitted by atmospheric discharges in the VHF 60-66 MHz band. It provides […]

The project aims to better understand small-scale processes to improve fog forecasts.It is supported by the ANR (SoFog3D project) and is part of the Contract of Objectives and Performance 2017-2021: […]

One of the largest challenges facing environmental science is understanding future changes in the terrestrial water cycle and the subsequent impact on water resources. It has also been recognized by […]

Objectives of the project The objective of the ICE-GENESIS project is to better simulate icing phenomena on aircraft. Within the framework of this project, a measurement campaign to study snow […]

HyMeX aims at a better understanding, quantification and modelling of the hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean, with emphasis on the predictability and evolution of extreme weather events, inter-annual to decadal […]

Abstract The first overarching objective of the Clouds-Atmospheric Dynamics–Dust Interactions in West Africa (CADDIWA) airborne campaign is to assess dust aerosol related effects, namely the direct radiative effect (DRE), the semi-direct radiative […]
The first AMMA observation campaign was successfully carried out from mid-January to mid-February. It enabled the characterisation of the microphysical and radiative properties of aerosols and their dynamics during the […]

The AEROCLO-sA project (AErosol, RadiatiOn and CLOuds in southern Africa) investigates the role of aerosols on the regional climate of southern Africa, a unique environment where natural and anthropogenic aerosols […]

EUREC4A, the Field Study, is an international initiative in support of the World Climate Research Programme’s Grand Science Challenge on Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity. EUREC4A will take place between […]

RALI-THINICE aims at investigating the dynamics of Arctic cyclones (ACs) and tropopause polar vortices (TPVs), as well as their interactions with cloud microphysics, the underlying sea surface and sea ice […]

Context: Lidar observations are the only means to reproduce highly resolved vertical profiles of key atmospheric parameters such as water vapour content, temperature, aerosols, and clouds. They also have great […]

The objective of MAP-IO is to study the composition of the atmosphere and the ocean-atmosphere processes that have an impact on regional climate and numerical weather prediction.This scientific programme is […]

Scientific background Clouds cover about 70% of the Earth’s surface and play a dominant role in the energy and water cycle of our planet. Only satellite observations provide a continuous […]

Over five years from 2013 to 2018, the DACCIWA project (Dynamics-Aerosol-Chemistry-Cloud Interactions in West Africa, funded by the EU) worked with partners in the region to improve understanding of the […]

Developed by CNES (Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales) in partnership with Eumetsat (EUropean organisation for the exploitation of METeorological SATellites), the IASI (Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer) instrument was designed for operational meteorology and for monitoring atmospheric chemistry and climate. IASI is a thermal infrared Fourier transform spectrometer that provides radiance spectra and derived atmospheric variables to feed operational weather forecasting centers, the Copernicus Services and the scientific community.

Megha-Tropiques is a space mission jointly managed by the space agencies CNES and ISRO. This mission is designed to study the convective systems of the atmosphere and more particularly the analysis of the water cycle through the transport and distribution of water vapor, the life cycle of convective systems and energy exchanges in the equatorial belt. The tropical zones are those where the most important energy exchanges occur: radiative exchanges, latent heat exchanges, transport of constituents and energy through dynamic processes. The challenge is therefore to increase knowledge of hydrological and energy processes in the tropics and their influence on the global circulation of the atmosphere, that the oceans, and climatic variations.

POLDER (POLarization and Directionality of the Earth’s Reflectances) instrument analyses the intensity and direction of light reflected by the Earth and its atmosphere, as well as its polarization, a physical characteristic describing how waves propagate. Such measurements reveal some interesting properties of clouds and aerosols, thereby telling us more about how they affect climate. Designed and developed by CNES, in close collaboration with the LOA atmospheric optics laboratory in Lille, the POLDER instrument is mainly dedicated to the study the of the clouds and aerosols properties, but it also provides valuable information on the directionality of terrestrial reflectances and on the ocean colour. It has been the first space instrument to provide global and systematic spectral, directional and polarization measurements of radiation reflected from the Earth and atmosphere.

Calipso is a joint Earth science mission between NASA and CNES dedicated to the measure of the vertical distributions as well as of the optical and physical properties of aerosols and clouds in the atmosphere, which influence the Earth’s radiation balance. For this purpose, it combines an active lidar instrument with passive infrared and visible imagers.

CloudSat is a NASA satellite. It is studying clouds in detail to better characterize the role they play in regulating Earth’s climate. It is providing a global survey of the vertical structure and overlap of cloud systems and their liquid and ice-water contents.

ACTRIS is a European research infrastructure that coordinates the acquisition and dissemination of measurements for the characterisation of ‘short-lived’ components of the atmosphere.The themes covered by this infrastructure are : […]

The project IAGOS (In-service Aircraft for a Global Observing System) is an European Research Infrastructure (ESFRI Roadmap 2006) conducting global longterm observations of atmospheric composition (reactives and greenhouse gases, aerosols, […]

