In meteorology, a parameter is a state of the atmosphere that can be quantified using measuring instruments. The states of these parameters have a direct impact on the evolution of future weather. There are four main parameters: temperature, measured with a thermometer; humidity, measured with a hygrometer; atmospheric pressure, measured with a barometer; and wind, measured with an anemometer.
The AERIS cluster brings together numerous projects studying various meteorological parameters, which you can find here :
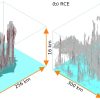
Scientific context C²OMODO (Convective Core Observations through MicrOwave Derivatives in the trOpics) is a CNES space project, a tandem of radiometers that will be launched in March 2030, as part […]

The dynamics of the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) form in response to synoptic flow and energy exchanges with the Earth’s surface. The height of the ABL defines the volume of air in […]

SAFRAN (developped at Meteo-France/CNRM) is a mesoscale analysis of near surface meteorological variables over France, at 8km for the spatial resolution and hourly for the temporal frequency and suitable for […]

ACTRIS-FR is the French component of ACTRIS-EU for the observation and exploration of aerosols, clouds and reactive gases and their interactions. ACTRIS is a distributed European research infrastructure supporting research […]

CAPITOUL is a coupled study of the urban atmosphere and the formation/transformation of urban aerosols, with a measurement campaign planned in the Toulouse region between March 2004 and March 2005. […]

AERIS provides access to radar data from the Météo-France French operational network in mainland France and overseas. The radar data is made up of four products: AERIS manages the conversion […]

AERIS provides access to observation data from the Météo-France ground weather observation network (RADOME and extended network) in France. Observation data from the ground network is made up of two […]
The CORSiCA Platform for Atmospheric Observations (PCOA) of the Aerology Laboratory is located in Corsica on about fifteen sites to respond to the different themes studied by participants from several […]
Since mid-2000, the interdisciplinary IMPETUS research project has been studying key aspects of the water cycle on the basis of two catchment areas in Benin and Morocco. The aim is […]
Scientific context: This project, endorsed by the WMO, brings together meteorological institutes and laboratories from about ten countries around the world. The scientific objective is to improve atmospheric models at […]

The prevention of heat-related risks and air quality in cities is a major public health issue. It is important to understand how people’s exposure to heat and air pollution varies […]

One of the largest challenges facing environmental science is understanding future changes in the terrestrial water cycle and the subsequent impact on water resources. It has also been recognized by […]

OBJECTIVES One of the important factors that determine the environmental impact of particles and gases is their atmospheric dispersion, which itself is largely controlled by the stability of the atmosphere. […]

Objectives of the project The objective of the ICE-GENESIS project is to better simulate icing phenomena on aircraft. Within the framework of this project, a measurement campaign to study snow […]

HyMeX aims at a better understanding, quantification and modelling of the hydrological cycle in the Mediterranean, with emphasis on the predictability and evolution of extreme weather events, inter-annual to decadal […]

La Cerdanya is one of the largest valley of the Pyrenees mountain range, spreading across Spain and France (between Occitanie and Catalunya). It is about 10 km wide and 35 […]

Objectives Growth of the convective planetary boundary layer (CBL) over land in the middle of the day due to solar heating of the Earth’s surface has been extensively observed and […]
The first AMMA observation campaign was successfully carried out from mid-January to mid-February. It enabled the characterisation of the microphysical and radiative properties of aerosols and their dynamics during the […]

STRATEOLE-2 is a project designed to study atmospheric events above the equator. The project is led by France and includes researchers in the United States and other countries. It consists […]

The MOSAI (Model and Observation for Surface-Atmosphere Interactions) project (ANR 2020) aims to assess and improve the interactions between the surface and the atmosphere in weather and climate numerical prediction […]

The PANAME (PAris region urbaN Atmospheric observations and models for Multidisciplinary rEsearch) initiative is a coordinating effort involving several ongoing multidisciplinary research projects that aim to gain a better understanding […]

What is the TIGR dataset ? The Thermodynamic Initial Guess Retrieval (TIGR) dataset, in its latest version, is a climatological library of 2311 atmospheric situations representative of the Earth’s atmosphere, selected […]

Developed by CNES (Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales) in partnership with Eumetsat (EUropean organisation for the exploitation of METeorological SATellites), the IASI (Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer) instrument was designed for operational meteorology and for monitoring atmospheric chemistry and climate. IASI is a thermal infrared Fourier transform spectrometer that provides radiance spectra and derived atmospheric variables to feed operational weather forecasting centers, the Copernicus Services and the scientific community.

GRUAN is an international reference network of about thirty stations dedicated to the observation of key climatological variables between the surface and the stratosphere by radiosoundings. Several French organisations have […]

The project The aim of the ARISE-FR project is to integrate observation and research activities on the atmospheric dynamics from the troposphere to the lower thermosphere in order to improve […]

